When it comes to heating and cooling your home or business, the options can be overwhelming. With rising energy costs and increasing interest in sustainable solutions, many are asking: should I choose a ductless heat pump or stick with a traditional HVAC system? The answer depends on your priorities, climate, and budget — and understanding the differences can save you thousands over the life of your system.
The biggest win for ductless systems is the elimination of duct losses, which can waste over 30% of a system’s energy in traditional setups.
Understanding Ductless Heat Pumps
Ductless heat pumps, also called mini-splits, deliver warm or cool air directly to individual rooms via wall-mounted units. They use an outdoor compressor connected to one or more indoor air handlers via refrigerant lines. Unlike traditional systems, they don’t rely on ducts, which can leak and waste energy.
These systems can achieve SEER2 ratings up to 28, compared to most traditional central systems ranging between 14–20 SEER2. That means they can be up to twice as efficient.
| Feature | Ductless Heat Pump | Traditional HVAC |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Up to 28 SEER2, 300% efficiency | 14–20 SEER2 |
| Energy Loss | Minimal (no ducts) | 20–30% loss via ducts |
| Installation | Easier, less invasive | Requires ductwork |
| Cost | $3,000–$5,000 per zone | Lower upfront |
| Flexibility | Zone control | Whole-house uniform |
By eliminating ducts, you avoid the 20–30% energy loss common in traditional systems. This alone can lead to significant savings over time. Additionally, ductless systems are ideal for additions, converted attics, or older buildings where installing ductwork would be impractical or prohibitively expensive. They also offer aesthetic flexibility with a variety of indoor unit designs, including ceiling cassette and floor-mounted options. This adaptability makes them suitable for both residential and commercial applications, ensuring that comfort can be tailored to specific spaces without compromising energy performance.
Efficiency and Operating Costs of a Ductless Heat Pump
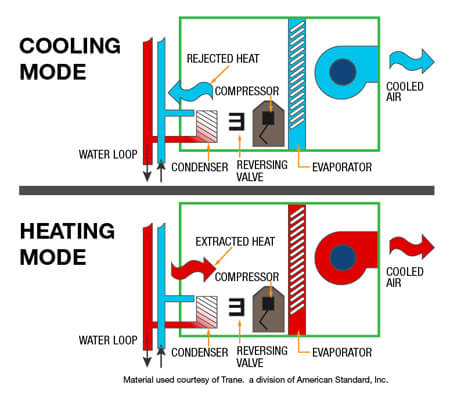
Heat pumps, including ductless models, can operate at up to 300% efficiency under optimal conditions. That means they produce three times more energy than they consume. This is possible because they move heat rather than generating it by burning fuel.
For homeowners and businesses, switching from a traditional central HVAC system to a ductless mini-split can reduce energy consumption by 25–40% due to zone control and elimination of duct losses. For example, if your annual heating and cooling costs are $2,000, a 30% reduction could save you $600 per year. You can explore more savings potential in our heat pump cost calculator.
With SEER2 ratings offering more accurate efficiency measurements, ductless mini-splits stand out as one of the most eco-friendly HVAC options for 2025.
These savings can be even greater in areas with high electricity rates or strong incentives for energy-efficient equipment. Rebates often range from $500 to $2,000 per unit. Over a decade, these savings can accumulate to thousands of dollars, especially if combined with smart thermostats that optimize usage. In commercial settings, the impact is multiplied, as businesses can significantly cut operational expenses while meeting sustainability goals. Maintenance costs also tend to be lower for ductless systems, since there are no ducts to clean and fewer mechanical components subject to wear.
Climate Suitability and Technological Advances in Ductless Heat Pumps
Ductless systems used to be recommended mainly for mild climates, but cold-climate models have changed the game. Modern units can maintain high efficiency at temperatures as low as -15°F, making them viable for much colder regions. For more tips on performance in extreme conditions, see our cold climate heat pump guide.
Manufacturers are also integrating smart technology into ductless systems. Built-in Wi-Fi and AI-driven climate control allow homeowners to optimize comfort and reduce energy use. Businesses benefit from zone-specific control, heating only occupied areas.
For example, a retail store might keep customer areas warm while reducing heating in storage spaces, saving on operating costs without sacrificing comfort. Some models now feature advanced defrost cycles and variable-speed compressors that adapt output to current conditions, further boosting performance. Additionally, noise levels have been reduced significantly, with many modern ductless units operating at under 25 decibels indoors, making them ideal for bedrooms, offices, and other quiet environments.
Real-World Ductless Heat Pump Applications and Case Studies
A Boston office retrofit replaced an aging central HVAC system with ductless VRF (Variable Refrigerant Flow) technology. The result? 38% lower energy use, reduced emissions, and a rapid ROI thanks to local incentives.
| Project | Savings | ROI |
|---|---|---|
| Boston Office Retrofit | 38% energy reduction | 3 years |
| Seattle Home Upgrade | 32% energy reduction | 4 years |
These examples highlight the flexibility of ductless systems. They can be scaled for both small homes and large commercial spaces. In residential applications, homeowners often report improved comfort due to precise temperature control in each room. In commercial cases, such as hotels, ductless systems allow individualized climate settings for each guest room, enhancing customer satisfaction. Furthermore, many retrofit projects benefit from minimal disruption during installation, allowing businesses to remain operational while upgrading their HVAC systems.
Installation Considerations for a Ductless Heat Pump
Ductless heat pumps are generally easier to install than traditional systems, especially in buildings without existing ductwork. Installers run small refrigerant lines through walls rather than constructing extensive duct networks.
However, each indoor unit covers a specific zone, so larger homes may require multiple units. This can increase upfront costs, although the long-term savings often outweigh them. For a breakdown of costs and payback, check our heat pump cost calculator.
In contrast, traditional HVAC systems provide uniform heating and cooling through ducts. This can be advantageous for large open spaces but less efficient for buildings with varied occupancy. It’s also important to consider aesthetics and placement; ductless units require visible indoor components, which may not appeal to everyone. Proper sizing and professional installation are critical to maximizing efficiency, as an incorrectly sized unit can lead to uneven temperatures and reduced lifespan.
Industry Trends and Future Outlook
The push for sustainability is driving innovation in heating and cooling. Federal and state programs continue to offer incentives for energy-efficient systems, and the Inflation Reduction Act has expanded these opportunities.
As more consumers value environmental impact, ductless heat pumps are poised to take a larger share of the market. Expect to see advancements in refrigerants with lower global warming potential and increased integration with renewable energy sources.
For instance, pairing a ductless heat pump with solar PV can drastically reduce energy bills and carbon footprint. Learn more about this approach in our article on solar heat pump systems. Analysts predict that by 2030, ductless systems could account for over 40% of residential HVAC sales in certain regions, driven by building code changes and consumer demand for high-efficiency solutions. As battery storage technology improves, the synergy between renewable energy and ductless heating/cooling will likely become even more attractive.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Ductless Heat Pump or Traditional System
Both ductless heat pumps and traditional HVAC systems have their merits. Ductless systems excel in efficiency, flexibility, and modern features, making them ideal for those prioritizing sustainability and long-term savings. Traditional systems may still be the right choice for large, uniformly heated spaces or where upfront cost is a major concern.
If you’re in a region with high energy costs or strong incentives, a ductless heat pump could be a smart investment. Consider your climate, building layout, and budget — and consult with an HVAC professional to assess your specific needs.
By weighing the benefits and trade-offs, you can choose a heating and cooling solution that delivers comfort, efficiency, and value for years to come. Remember that energy prices and technology are evolving, so what is optimal today may shift in the coming decade. Regularly reviewing your system’s performance and staying informed on new advancements will ensure you continue to enjoy the best possible balance of comfort, cost savings, and environmental responsibility.